Imagine waking up one morning, eager to start your day, only to discover that your knee feels achy and painful. It is a scenario many of us might face, whether it’s from dancing a bit too energetically or just from the wear and tear of daily life. You might wonder why your knee hurts so much. What causes the pain?
Table of Contents
Introduction
In this article, we will discover how knee pain happens by looking at the structure of the knee, causes of knee pain, who is most at risk, and ways to prevent and relieve the pain. Whether you’re dealing with a sudden ache or just want to avoid potential knee issues, we have got the information you need to manage and understand knee pain effectively.
Anatomy of the Knee
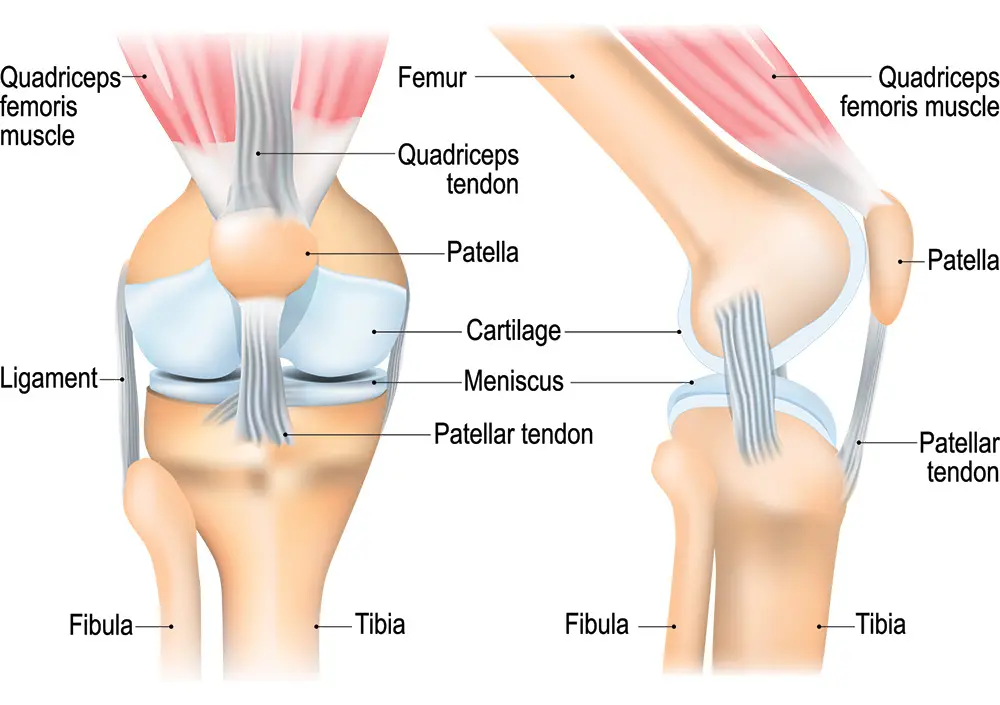

The knee is a complex joint that supports the lower body and leg, providing stability and mobility. It has three main bones: the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap). These bones are connected by ligaments and cartilage. The knee’s primary functions include supporting the body when standing, aiding in movements like raising or lowering, allowing leg twisting, and acting as a shock absorber.
Some of the structure of the knees include:
- Patella: Covered with the thickest cartilage in the body, It can endure intense stress.
- Meniscus and Articular Cartilage: Both act as shock absorbers, and cushions between the bones, enabling smooth movement.
- Ligaments: Four key ligaments—anterior cruciate, posterior cruciate, medial collateral, and lateral collateral—stabilize the knee and prevent excessive movement.
- Tendons: Connect muscles (hamstrings and quadriceps) to bones, helping knees to bend its placement.
- Bursa: Fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction and inflammation within the knee joint.
Understanding the structure of the knee can help identify the source of pain and target treatment effectively.
Causes of Knee Pain
As aforementioned, our knees’ problem can be identified based on its anatomy. Some of the common causes are;
Arthritis
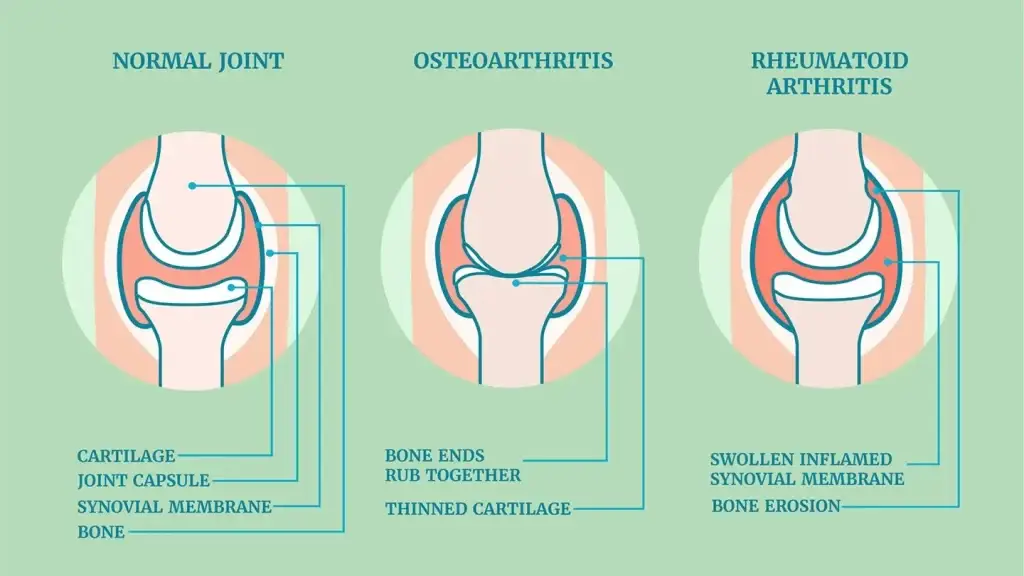
Arthritis is a disease that affects your joints. Arthritis cause inflammation and swelling of the joints, causing people to feel pain and stiffness.
Two common types of arthritis are;
- Osteoarthritis
This is most common arthritis and long-term joint condition, and usually it affects individuals above 45 years old. In the US, this type of arthritis affected over 32 million adults.
Osteoarthritis happens when the cartilage between joint wears down, causing the bones to rub against each other. People with osteoarthritis often experience pain, inflammation, warmth and redness around the knee.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis happens when our immune system attacks our own body’s tissues. This affects the lining of the joints, causing a painful swelling that erodes the bone and joint deformity. The attack causes uncontrolled inflammation that damages cartilage, which in turns damage the joints.
In addition to these, people can also experience less common types of arthritis, such as gout and septic arthritis.

Overused Injuries
Knee pain can occur when there is repeated stress on our knee joints. Most people who have this injury got it from high-impact sports like running, skiing, and jumping. As the knees received prolonged pressure, it results in irritation and inflammation to the knee.
Overuse injuries of the knee include:
- Bursitis
- Tendinitis
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
Trauma and Injuries
- Sports Injuries
Athletes are at high risk for knee injuries regardless of what kind of sports they play. One might suffered from either ligament injuries, or meniscus tear or bursitis and tendonitis or knee dislocations. Fret not, many knee injuries are treatable depending on the severity of the injury.


| Ligament Injuries | ACL injury: the ligament in the centre of the knee. ACL controls the forward movement and rotation of the shin. ACL injury may occur because of sudden stops or changes in direction. PCL injury: The PCL controls the backward movement of the knee. However, this ligament can also tear after a heavy impact on the knee. LCL Injury: LCL controls knee stability. However, repeated twisting can injure the LCL. MCL injury: MCL located at the outer side of the knee. It also controls stability and can sustain an injury after receiving a blow. |
| Meniscus Tear | Meniscus is a cartilage that helps to absorb shock and stabilize the joint. A torn meniscus causes pain, swelling, and stiffness. An individual with meniscus tear also encounters trouble to extend their knee fully. Some signs and symptoms of meniscus tear are: · A clicking or popping sensation in the knee · Swelling on the knee · Pain especially when doing any movement · Difficult to fully straighten or bend the knee · Feel like your knee losing its control. |
| Bursitis and Tendinitis | Inflammation of the bursa or tendons can lead to long-lasting pain and swelling. It may also cause tendon tears. This is more common in older people or those with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes. The inflammation can also lead to a chronic pain, swelling and the worst, tendon tear apart from the bone. Hence, it is crucial to seek treatment from a doctor as early as possible to avoid serious damage. |
| Knee Dislocations | Occur when the femur or tibia are misaligned as a result from trauma. They are extremely painful and require immediate medical attention. Depending on the damage, treatment may include realigning the bones or using a splint. Doctors may need to perform surgery for broken bones, torn ligaments, or damaged blood vessels and nerves. |
Who is At Risk to Get Knee Pain?
Older People


Older people often get osteoarthritis. This happens because their muscles and joints change over time. These changes result in damage to the cartilage in their joints, reducing the joint’s ability to absorb shocks, resulting in knee pain and stiffness.
The muscles around the knee also weaken and reduce the support for the joint, enhancing the risk for osteoarthritis.
Athletes


Frequently, athletes participate in high-intensity sports. Activities such as running, jumping, and twisting can put heavy stress on the knee joints. This can cause damage to the cartilage over time.
Obese People


Obesity increases the knee pain as additional body stress is placed on the knee joints, especially when moving. Excess fat also increases the production of inflammatory chemicals that contributes to inflammation, which causes pain on the knee.
Past Injuries
A person with a history of knee injury may be vulnerable to future injuries or stress, as the damage from past injuries can persist even after initial healing. This persisting damage, along with weakness and instability, makes the knee more susceptible to re-injury and strain.
How to Prevent Knee Pain
- Low-Impact Exercise
- Stretching before and after exercise
- Avoid wearing high heels for long periods
- Keep ideal weight
- Correct your posture


Knee Pain Treatment
A person can choose to relieve pain at home or with medication. Some of these treatment options include:
1. R.I.C.E Method
R.I.C.E. is an acronym for a set of steps designed to reduce knee pain. Follow these steps to help alleviate discomfort and promote healing;
- R: Immediately stop any activity on your knee, lie down and let your knee rest from any movement.
- I: Put an ice pack on the affected knee to reduce inflammation and swelling.
- C: Use elastic bandage and wrapped around the effected knees to compress the knee to bring down swelling.
- E: Raise the effected knee a bit higher than the level of the head (while lying down).


2. Exercise
It might sound almost ridiculous, but if you have knee pain, one of the best ways to relieve it is through exercising.
One might think “I barely can move my leg, much more exercising? You want me to run and suffer, don’t you?”
The exercise is not vigorous like running, swimming or playing sports etc, but stretching exercise.
Some of the best strengthening exercises are
- Half squat
- Calf raises
- Hamstring curl
- Leg Extensions
- Straight leg raises (Knee Friendly)


3. Rehabilitation / Physiotherapy
Rehabilitation helps strengthen the muscles around the knee, and provide better support and stability for the knee joint. Physiotherapy helps in building flexibility and improve range of motion of the knees.
4. Pain Reliever
One might opt for medication such as NSAIDs to gain relieve pain immediately. NSAIDs reduce pain and swelling by blocking chemicals that cause inflammation in the body, especially in the knee.


5. HA Injection
Hyaluronic acid injection is used to treat knee pain from osteoarthritis to patients who show no responses to pain relievers and other treatments. HA injection increase the fluid in the joint, which reduce friction between the bone and act as anti-inflammatory.
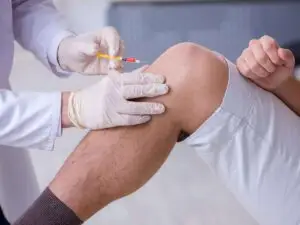

6. Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement (TKR) is a surgical procedure where damaged bone and cartilage in the knee are removed and replaced with artificial components to lessen pain and restore joint function.
It is usually suggested for serious arthritis or knee injuries that did not improve with other treatments. Recovery includes rehabilitation to rebuild strength and movement.
Conclusion
Knee pain can be annoying, but knowing its causes and how to handle them is the first step towards relief and recovering. Whether it’s occasional discomfort or to prevent future knee problems, taking preventive measures is crucial.
If the pain continues, it’s important to see a doctor for a complete diagnosis and proper treatment. Taking these steps will help you manage knee pain more effectively and support your journey towards a healthier, more active life.
You Can Also Read This Article in Bahasa Malaysia Here
No ONE DESERVE TO LIVE IN PAIN
Experience the Difference with Klinik Tuah’s Knee Pain Treatment